How to Protect Animal Welfare in Slaughterhouse Design?
Discover effective strategies on how to protect animal welfare in slaughterhouse design for a more humane approach to livestock processing.
11 September, 13:09
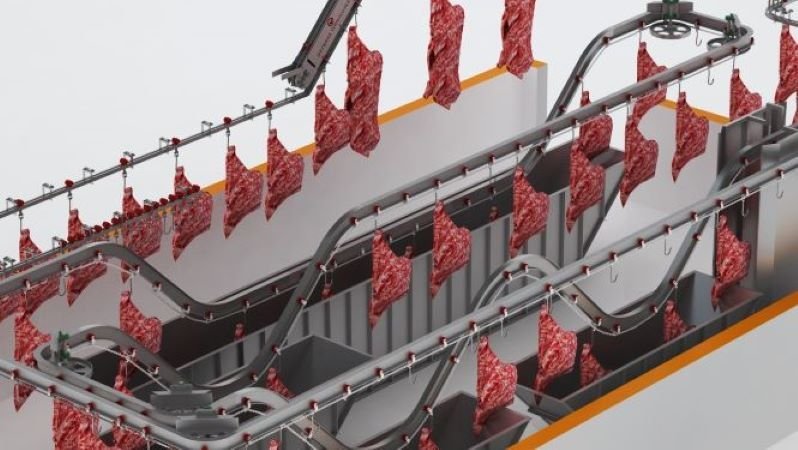
Designing a slaughterhouse is not only about efficiency and productivity — it is also deeply tied to ethics, animal welfare, food safety, and sustainability. Modern consumers and regulatory bodies increasingly demand that slaughterhouse facilities respect animal welfare standards from the moment animals arrive until processing is complete. A well-designed slaughterhouse can significantly reduce stress, pain, and fear for animals while also improving meat quality and ensuring compliance with international standards.
Why Animal Welfare Matters in Slaughterhouse Design
Protecting animal welfare in slaughterhouses is crucial for several reasons. Animals should be treated with dignity and respect at every stage of the process to ensure ethical standards are upheld. When animals experience stress and suffering, it can directly affect meat tenderness, color, and safety, compromising the quality of the final product.
Moreover, compliance with international standards such as OIE (World Organisation for Animal Health), EU directives, and local animal welfare laws mandates humane handling and slaughter practices. These regulations are designed to protect animals and promote better practices within the industry. In today's market, modern consumers increasingly prefer meat sourced from facilities that value humane treatment and transparency, making animal welfare not just a moral obligation but also a significant factor in consumer choice.
Key Design Principles for Protecting Animal Welfare
Stress-Free Animal Handling
Modern slaughterhouse design should minimize stress during transport and unloading. Features such as non-slip flooring, curved chutes, and well-ventilated holding areas ensure smooth animal movement. These elements work together to create an environment that prioritizes animal welfare. Curved alleys, popularized by animal welfare expert Dr. Temple Grandin, play a crucial role in reducing stress. By preventing animals from seeing what lies ahead, they help diminish fear and resistance during the handling process.
Adequate Space and Comfort in Holding Areas
Holding pens should provide sufficient space, fresh water, and appropriate resting conditions to ensure the well-being of the animals. Ample space allows them to move freely, reducing stress and promoting a sense of security. Proper lighting and ventilation are crucial as they help reduce stress and maintain the animals’ natural circadian rhythm. These environmental factors contribute significantly to the overall comfort of the animals in the holding areas. Additionally, separation of species is important to prevent aggression and injuries among different animals.
Noise and Lighting Control
Excessive noise and sudden changes in lighting can cause panic in both animals and humans. To create a calm environment, facilities should prioritize the use of low-noise equipment that minimizes disturbances. This approach helps in reducing stress levels and promotes a sense of safety. Additionally, maintaining consistent, soft lighting is essential. By avoiding abrupt changes, facilities can help prevent anxiety in animals. Proper lighting design, which eliminates shadows and dark spots, encourages animals to move calmly without resistance, allowing for smoother interactions and better overall welfare.
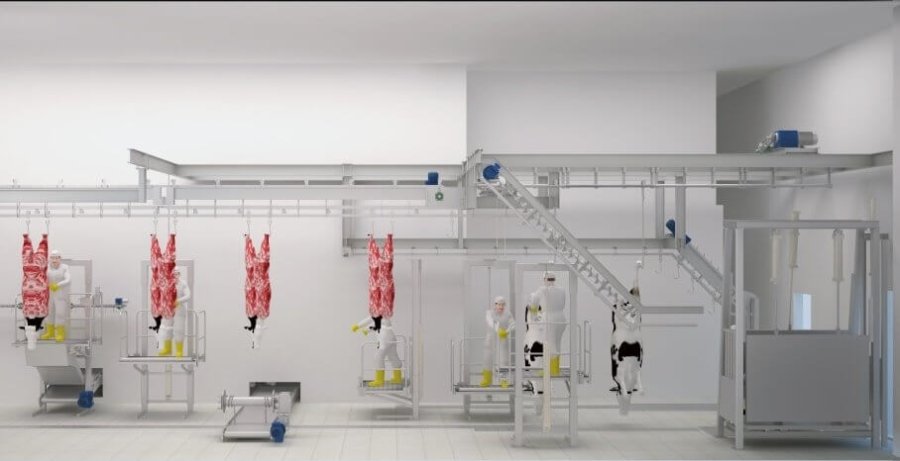

Humane Restraint Systems
Animal restraint should never involve excessive force. The welfare of the animal is paramount, and modern systems have been developed to ensure this. These systems utilize gentle restraining boxes or conveyor restrainers that are specifically designed to support the animal’s body without causing pain or distress. By prioritizing the animal's comfort and safety, these innovative solutions allow workers to handle animals efficiently while maintaining a humane approach.
Proper Stunning Methods
Humane slaughter requires effective stunning before bleeding to ensure the welfare of animals. Proper stunning methods are essential to render animals unconscious instantly, minimizing any distress or pain. Common methods include captive bolt stunning, which uses a mechanical device to deliver a swift blow to the animal's head, and electrical stunning, where an electric current induces immediate unconsciousness. Additionally, controlled atmosphere stunning (CAS) involves altering the environment to induce a state of unconsciousness through gas mixtures.
Hygiene and Safety Standards
Animal welfare is linked to food safety, emphasizing the importance of maintaining high standards in meat production. A clean, well-designed facility is essential as it prevents cross-contamination and ensures the delivery of high-quality meat products. To achieve this, slaughterhouse design should incorporate easy-to-clean materials that facilitate sanitation processes.
Efficient drainage systems are crucial in managing waste and preventing the buildup of contaminants. Furthermore, implementing strict biosecurity measures protects both the animals and the end consumers, reinforcing the connection between humane treatment and food safety.
Innovative Approaches in Slaughterhouse Design
Innovative approaches in slaughterhouse design are transforming the industry by prioritizing animal welfare and operational efficiency. One of the key advancements is the integration of technology that reduces human error and ensures consistent, humane handling. With the use of advanced cameras and sensors, facilities can monitor animal behavior in real time, effectively detecting signs of stress or mishandling before they escalate into more serious issues. Another significant development is the adoption of smaller, mobile facilities that allow animals to be processed closer to farms. This innovative design minimizes transport stress, ensuring a more humane experience for the animals. Furthermore, these facilities often incorporate renewable energy and waste recycling systems, which not only enhance operational sustainability but also align with broader environmental and welfare goals.
